STAGE 3_2024
In the third phase of the project, we aimed to identify the modifications in the gene expression patterns triggered by ELK3 overexpression and knockdown, in a genomic approach, in order to determine the main molecular mechanisms by which this transcription factor affects TNBC metastasis. The rationale behind this objective is to group the genes that are modulated by ELK3 into signaling pathways associated with BC metastasis, by overlapping the results obtained for ELK3 overexpression with the ones obtained for ELK3 knock down.
We evaluated the expression level for all the genes in the human genome by a holistic functional genomic approach, using the microarray technology, starting with the total RNA extracted from one of the cell lines in which the ELK3 transcription factor is down-regulated. The expression levels of some of the genes from the microarray data were also validated by RT-qPCR in both transformed (ELK-OE and ELK-KD) and parental cell lines.
In the microarray analysis of MDA231_ELK-KD1 vs. MDA231_CTR-KD, we identified 740 genes modulated by the inhibition of the ELK3 transcription factor (FR > ±1.3, p<0.05), of which 322 were overexpressed and 418 were downregulated. The top 50 upregulated and downregulated genes based on the microarray data, plotted for each biological replicate, are shown in Figure 1.
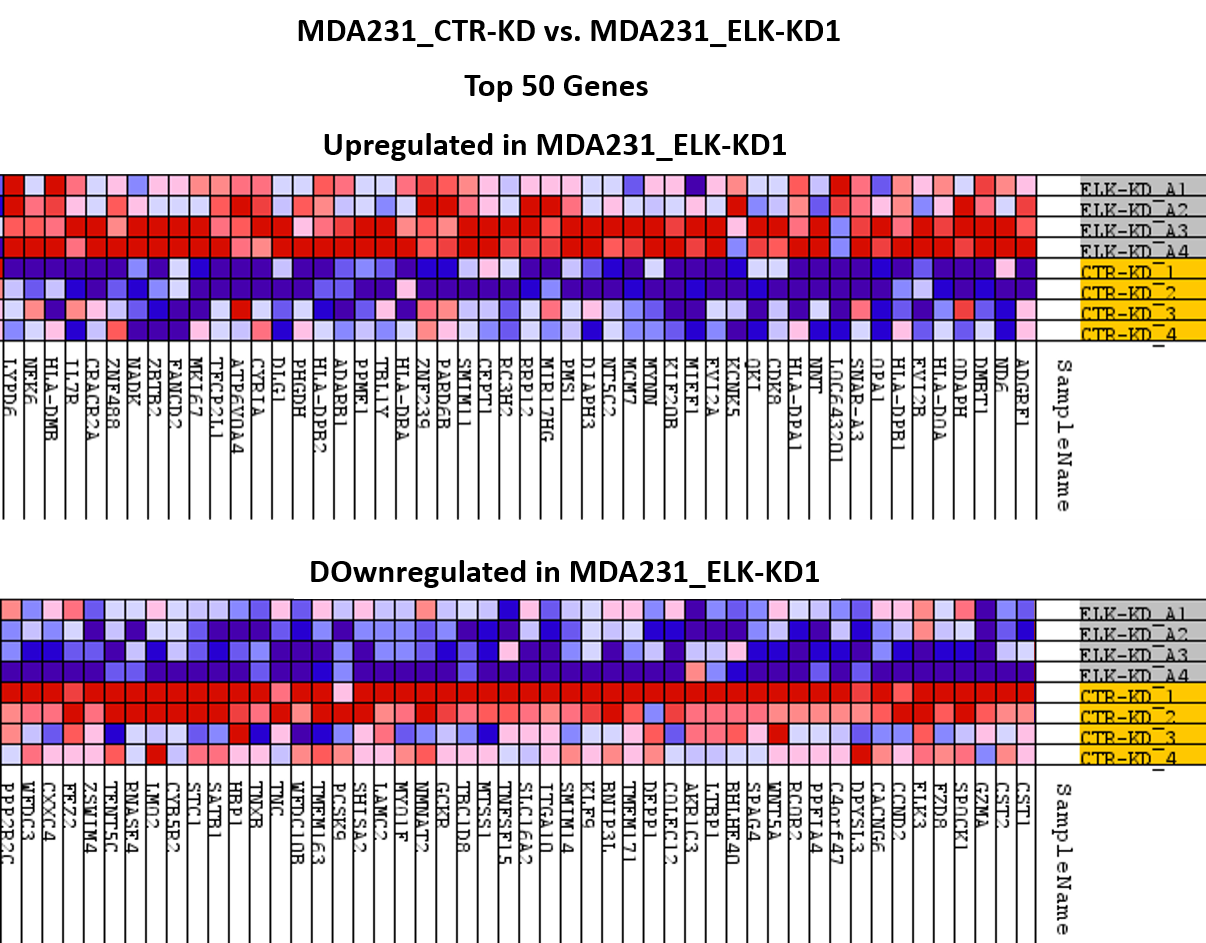 Fig. 1 Top 50 upregulated and dowregulated genes following ELK3 inhibition (MDA231_ELK-KD1 vs. MDA231_CTR-KD), based on microarray data, represented for each biological replica (images created in GSEA_4.3.0 software).
Fig. 1 Top 50 upregulated and dowregulated genes following ELK3 inhibition (MDA231_ELK-KD1 vs. MDA231_CTR-KD), based on microarray data, represented for each biological replica (images created in GSEA_4.3.0 software).
The whole set of differentially expressed genes (n=740) obtained in the microarray analysis were used for the functional analysis in Ingenuity Pathway Analysis Software (IPA). Functional analysis in the IPA software revealed 43 cellular processes affected by ELK3 transcription factor inhibition, 22 of which are related to cancer. The main cellular processes triggered by the inhibition of the ELK3 transcription factor were the inhibition of cell invasion and migration and the inhibition of the self-renewal capacity of cells, doubled by the induction of apoptosis, with the impairment of cell viability, demonstrating, on the molecular level, the cellular processes induced by ELK3 in our cell lines. Therefore, we are now able to present the main molecular mechanisms by which ELK3 impacts TNBC metastasis in terms of cell motility and and stemness potential.
We evaluated the expression level for all the genes in the human genome by a holistic functional genomic approach, using the microarray technology, starting with the total RNA extracted from one of the cell lines in which the ELK3 transcription factor is down-regulated. The expression levels of some of the genes from the microarray data were also validated by RT-qPCR in both transformed (ELK-OE and ELK-KD) and parental cell lines.
In the microarray analysis of MDA231_ELK-KD1 vs. MDA231_CTR-KD, we identified 740 genes modulated by the inhibition of the ELK3 transcription factor (FR > ±1.3, p<0.05), of which 322 were overexpressed and 418 were downregulated. The top 50 upregulated and downregulated genes based on the microarray data, plotted for each biological replicate, are shown in Figure 1.
 Fig. 1 Top 50 upregulated and dowregulated genes following ELK3 inhibition (MDA231_ELK-KD1 vs. MDA231_CTR-KD), based on microarray data, represented for each biological replica (images created in GSEA_4.3.0 software).
Fig. 1 Top 50 upregulated and dowregulated genes following ELK3 inhibition (MDA231_ELK-KD1 vs. MDA231_CTR-KD), based on microarray data, represented for each biological replica (images created in GSEA_4.3.0 software).The whole set of differentially expressed genes (n=740) obtained in the microarray analysis were used for the functional analysis in Ingenuity Pathway Analysis Software (IPA). Functional analysis in the IPA software revealed 43 cellular processes affected by ELK3 transcription factor inhibition, 22 of which are related to cancer. The main cellular processes triggered by the inhibition of the ELK3 transcription factor were the inhibition of cell invasion and migration and the inhibition of the self-renewal capacity of cells, doubled by the induction of apoptosis, with the impairment of cell viability, demonstrating, on the molecular level, the cellular processes induced by ELK3 in our cell lines. Therefore, we are now able to present the main molecular mechanisms by which ELK3 impacts TNBC metastasis in terms of cell motility and and stemness potential.
